he human species multiplied after agriculture increased the supply of food.after food increased, the population increased to about 5 million from 4 million. the concentration of large numbers of people in villages encouraged specialization of labor. most people in neolithic villages cultivated crops or kept animals. but a surplus of food enabled some individuals to concentrate their time and talents on enterprises that had nothing to do with the production of food. the rapid development of specialized labor is apparent from excavations carried out at the one of the best known neolithic settlements, Catal Huyuk. in this city, many remains of pots and jewelry were found. pottery was need when the surplus of food went up because the pots were good storage of surplus food. the pots also held liquids for storage and transporting them. metalworking increased by increase of population. more tools were needed to hunt the food and to gather crops as well.
Wednesday, September 21, 2011
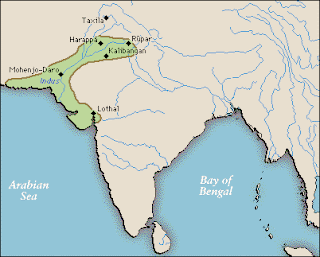
early region of state: nile valley
- Nile valley is noted for their dense populations, urbanization processes, and cultural innovation. The initial formation of these civilizations is based on the movement of peoples into the river valleys and plains. Egypt and the Nile Valley civilizations were defined by the rich alluvial soils that annual floods deposited along the Nile banks and in the delta and the flood plains. The use of water and the timing of flood seasons gave rise to a number of technological innovations, such as the calendar. These cultural and technological innovations also guaranteed the growth of large populations and increased the possibility that some of those populations would be located in central urban centers.
early region of state: babylonia
- most prominent of the later conquerors was the Babylonian Hammurabi, who styled himself as “king of the four quarters of the world”. the Babylonian empire dominated Mesopotamia until about 1600 B.C.E. Instead of traveling from city to city with a army, Hammurabi ruled from Babylon and stationed deputies in the territories they controlled.
early region of state: mesopotamia
- Mesopotamia- means “land between the rivers”. artificial irrigation led to increased food supplies, which in turn supported a rapidly increasing human population and attracted migrants from other regions. Sumerians were the first people to inhabit land around the sixth millennium B.C.E. the wealth of the sumer attracted migrants from other regions. Sumerians built the world’s first cities as the population was increasing. these cities were different from neolithic ones. were more organized and centered around politics and military. once Mesopotamia had organized effective states, conflicts between city-states often led to war. in efforts to move beyond these constant conflicts, a series of conquerors worked to establish order on a scale larger than the city- state by building empires that supervised the affairs of a lot of people and cites. these regional empires emerged as Semitic peoples like the Akkadians and the Babylonians of northern Mesopotamia began to overshadow the Sumerians.
Arts and Artisanship
for sculptures, pottery would be a good example. Sculptures of pots were made for decorations, and later storage. The pots stored food until ready for use. Later on they were used to hold liquids and transport liquids to different parts of the villages. Paleolithic had no use for pottery but when the surplus of food came around, neolithic did use them. certain religions had certain gods they worship, so different sculptures were made. So religion determines how the sculptures are made and designed. Also political issues cause how sculptures and paintings are created. Paintings could be of king, or emperors of a certain area.
culture to literature
without culture, there wouldnt be literature. Literature includes language and writing which can make the difference between certain cultures. When a group of people who speak the same language, tend to adapt to the same things and act a like. That can create a whole new culture.
New religious beliefs
Hebrew, vedic religion, and Zoroastrianism are new religious beliefs developed in this period and continue to have strong influences in later periods. the earliest Hebrews were pastoral nomads who inhabited lands between Mesopotamia and Egypt during the second millennium B.C.E. The Hebrew had a story of the version Epic of Gilgamesh. According to their scriptures, some Hebrews migrated from Palestine to Egypt during the 18th century B.C.E.Hebrew has really strong influences in later periods because it led to Jerusalem, Christianity, wars, battles, and new religions branching out from its self.
Introduction!
Welcome! this blog shows pictures of core civilizations, early regions of empire building, examples of art, and new religious beliefs. We hope you enjoy and learn information about these topics that you never knew before!
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)